用 Class.forName 与用 ClassLoad 加载类之间有什么区别?
时间:2018年10月11日
JDK 版本:1.8
1. 源码分析
在分析两者之前,先来看看 java 类加载的过程。
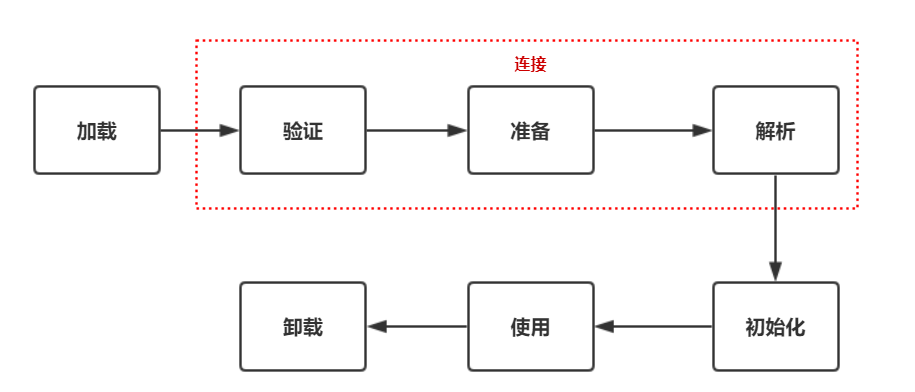
- 加载:JVM 将 class 字节码文件加载到内存中,并将这些静态数据转换成方法区的数据,在运行时数据区堆中生成一个表表这个类的 java.lang.Class 对象,作为方法区类数据的访问入口。
- 连接:执行下面的校验、准备和解析步骤,其中解析步骤是可选的。
- 验证:检查加载的 class 文件的正确性和安全性。
- 准备:为类变量分配存储空间并设置类变量初始值,类变量随类型信息存放在方法区中,生命周期很长,使用不当和容易造成内存泄漏。
- 解析:JVM 将常量池内的符号引用转换为直接引用
- 初始化:执行类变量赋值和静态代码块
- 使用
- 卸载
Class.forName()
forName(String) 方法:
@CallerSensitive
public static Class<?> forName(String className)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass();
return forName0(className, true, ClassLoader.getClassLoader(caller), caller);
}
内部调用了 forName0
private static native Class<?> forName0(String name, boolean initialize,
ClassLoader loader,
Class<?> caller)throws ClassNotFoundException;
forName0 是一个本地方法,第二个参数是 boolean initialize,这里传递的是 true,所以 forName(String) 这个方法在加载类的时候会初始化类。
ClassLoad
看看 ClassLoad.loadClass(String) 这个方法。
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
内部调用 loadClass(String, boolean)
/**
* @param name,被加载的类的全限定名称
* @param resolve,是否将类进行解析
*/
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException
{
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
long t0 = System.nanoTime();
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ClassNotFoundException thrown if class not found
// from the non-null parent class loader
}
if (c == null) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
c = findClass(name);
// this is the defining class loader; record the stats
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getParentDelegationTime().addTime(t1 - t0);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClassTime().addElapsedTimeFrom(t1);
sun.misc.PerfCounter.getFindClasses().increment();
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
看了源码,我们可以知道 forName 在加载类的时候会将其初始化,而 loadClass 是不会把类初始化。
2. 实例对比
为了讲述例子,下面将通过两种不同的方式来将 SelfClass 类加载进来。
package com.learnclass;
public class SelfClass {
static{
System.out.println("SelfClass has been created!");
}
public void say() {
System.out.println("hello, this is self class.");
}
}
2.1 Class.forName 加载类
forName(String) 得到的 Class 是已经初始化过的。
可以看看下面的测试用例:
package com.learnclass;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNotNull;
public class ClassTest {
@Test
public void forNameTest() throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class selfClass = Class.forName("com.learnclass.SelfClass");
assertEquals("SelfClass", selfClass.getSimpleName());
}
}
输出结果:
SelfClass has been created!
为了做个对比,添加了下面的测试用例,看看正常的初始化 SelfClass。
@Test
public void normalInitTest() {
SelfClass instance = new SelfClass();
}
输出结果:
SelfClass has been created!
可以看出,两者的结果是一样的。
2.2 ClassLoad 加载类
@Test
public void classloadTest() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
Class selfClass = classLoader.loadClass("com.learnclass.SelfClass");
assertEquals("SelfClass", selfClass.getSimpleName());
SelfClass instance = (SelfClass) selfClass.newInstance();
assertNotNull(instance);
}
没有任何输出。